It is a natural physiological process in men to allocate a small amount of urine. This is a type of lubricant that is obtained as a result of the work of the glands concentrated on the head of the penis. Abundance, heterogeneous consistency and cloudy color are signs of pathological disorders of the urogenital system.
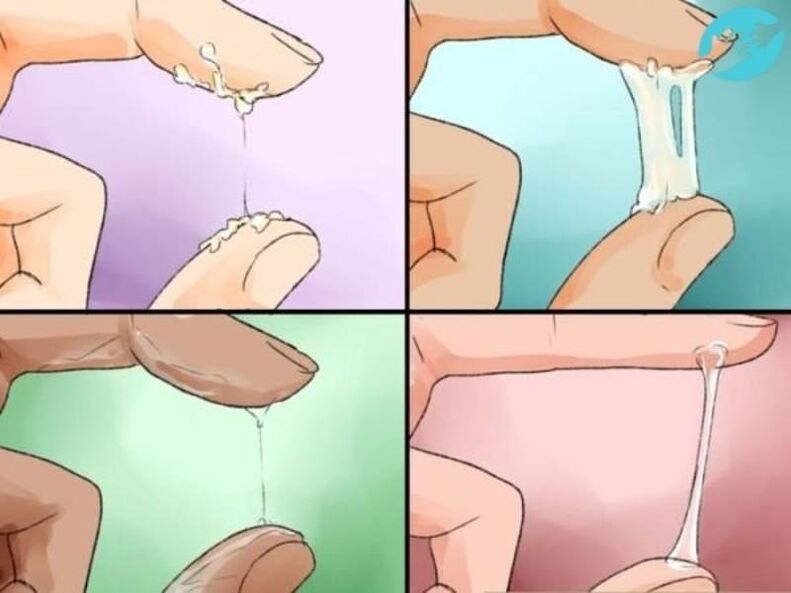
A change in the color, texture or quantity of the urethra in men indicates the presence of a disease of the urogenital system
Normal discharge in men
A whitish or colorless fluid is constantly present on the foreskin of the penis. It can gradually come out of the urethra under pressure, sometimes spontaneously.
table "Criteria for normal discharge in men"
| Type of issue | Typical |
|---|---|
| Smegma | The lubricant is produced by the glands in front of the skin, has a cream consistency, and is white in color, sometimes with a yellow or green tint. The secret of fat and bacteria residues prevents friction between the foreskin and the head. The abundance depends on age - the largest amount of fluid in adolescence, and the smallest in old age (practically absent) |
| Colorless discharge that looks like clear mucus (libido urethrorhoea) | Mucus is produced by the urethra and bulbourethral glands during an erection (when aroused). Their purpose is to lubricate the urethra so that the seminal fluid can pass through it unimpeded. The amount of discharge is usually small, but it can increase depending on sexual abstinence (the less often a man lives, the more abundant the pre-ejaculatory secret is - sometimes it drips from the penis). Is it possible to get pregnant from such discharge? Practically not, because they contain too little sperm. But after the eruption of the seminal fluid, repeated unprotected intercourse can lead to conception |
| Ejaculation (emission) not related to sexual contact | Spontaneous ejaculation occurs in the morning (the highest level of testosterone in the blood). A similar phenomenon occurs during sleep. Environmental pollution is most often observed in adolescence, but it can also occur in adult men who do not have a regular sex life. |
| Clear discharge from the urethra (prostorrhea) | The secretion is composed of sperm and prostate secretion. The liquid leaves the urinary canal with strong tension when defecating or coughing. Glassy discharge from the penis occurs even after passing urine - this is a normal phenomenon |
The first symptom of urogenital pathologies is the darkening of secretions or the acquisition of an uncharacteristic shade. Violations can be accompanied by a change in the color of urine, pain in the lower abdomen, and discomfort in the genitals.
Causes of discharge from the urethra
Genital pathogens, non-specific infections, malignant tumors, mechanical injuries (injuries, surgeries) can cause atypical discharge from the penis. The nature of discharge from the penis depends on the specific pathology of the urogenital system.
Inflammatory processes
Inflammatory foci can be caused by a violation of the microflora of the genitals, which is caused by opportunistic organisms - staphylococcus aureus, Candida fungus, Escherichia coli. Such bacteria are always present in small quantities on the mucous membrane of the foreskin, and with a decrease in immunity (long-term use of antibiotics, moral exhaustion or hypothermia of the body), they actively develop, provoking serious diseases.
- Thrush. This pathology is characterized by curd-white discharge with white pellets similar to cottage cheese. The secret abounds in an unpleasant sour smell. During ejaculation or urination, the man feels a burning sensation in the penis, pain and pain in the groin.
- Inflammatory foreskin lesiondiffers from purulent jelly-like secretions by the smell of putrefaction. At the same time, severe redness and pain appear on the head.
- Urethral gardnerellosis. The nature of the selected liquid is scarce, it smells like rotten fish, and is green or yellow in color.
- Prostatitis. The selected fluid is cloudy and appears at the end of urination. In the acute course of the disease, the abnormal secretion from the penis is abundant, and in the chronic period it is scarce. In addition to atypical secretions, the man also struggles with urination difficulties and groin pain.
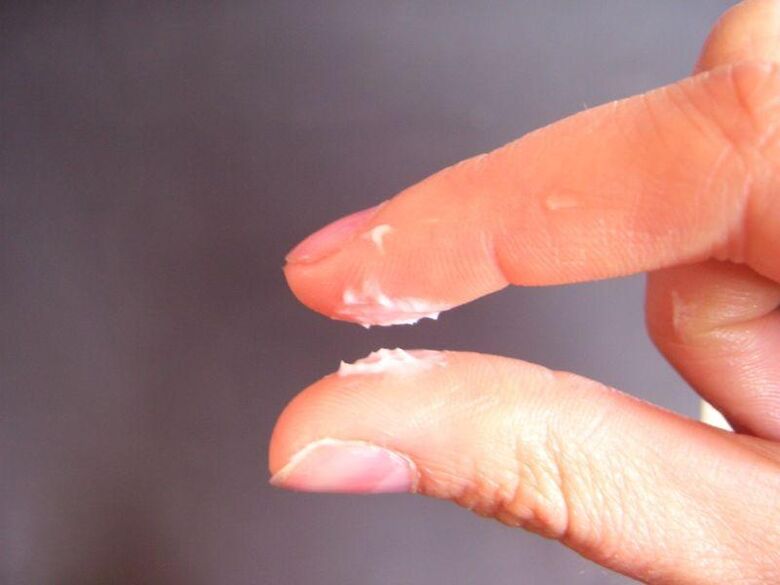
Non-specific inflammations are not sexually transmitted. The source of their occurrence is an imbalance of the urogenital flora.
Non-inflammatory pathologies
Pathological secretions can be provoked by chronic diseases or injuries not only to the genitals, but also to the spine, nervous system, and constant stress.
- Haemorrhoea- the condition is characterized by bleeding without blood clots. The cause can usually be mechanical damage (trauma, catheter insertion, removal of flora). In this case, the selected blood stops quickly and without clots. In the case of small stones passing out, blood-tinged mucus is present from the urethra after or during bladder emptying.
- Spermatorrhoea- involuntary ejaculation outside of sexual intercourse or masturbation. The reason for the whitish discharge is a weakening of the tone of the semispheric tubules, a violation of the innervation.
- Oncological neoplasms in the organs of the urogenital system. The brown discharge contains blood clots, has a slimy consistency, has purulent inclusions and a corresponding odor.
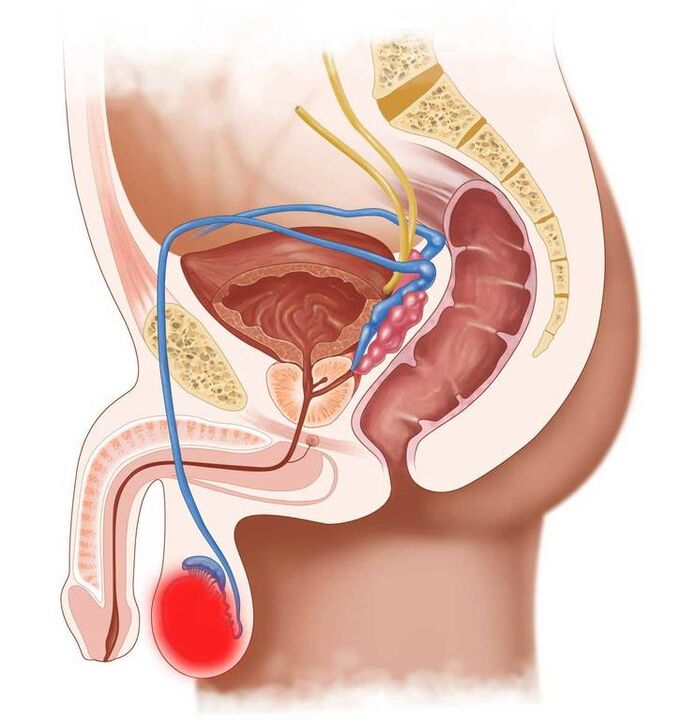
Problems related to the contraction function of the smooth muscles of the bladder, in the case of a benign tumor of the prostate, the discharge is white or transparent, liquid and abundant, but odorless.
sexually transmitted infections
The first symptom of sexually transmitted diseases is an abnormal discharge from the penis. Their nature depends on the pathogen:
- Foamy, colorless or whitish mucus containing pus appears as a result of exacerbation of mycoplasmosis, ureaplasmosis or chlamydia. There are especially many plaques on the head of the penis affected by chlamydia.
- A small amount of clear and sticky fluid is a symptom of chronic chlamydia infection, mycoplasmosis or ureaplasmosis.
- Green or yellow mucus with a strong odor is a sign of gonorrhea. The discharge in this case is sticky and abundant, with a thick consistency. The disease causes great discomfort - the genitals hurt, itch and spin, especially when urinating.
Important!
The amount, color and smell of discharge from the penis can change with neglect of the disease. Infections are often combined (gonorrhea and trichomoniasis, ureaplasmosis and mycoplasmosis), which aggravates the patient's condition. In case of unnatural fluid coming from the penis, consult a professional immediately.
Which doctor should I see?
Uncharacteristic urethral discharge, difficulty emptying the bladder, and lumbar pain are symptoms that should be taken to the hospital immediately. A urologist deals with diseases of the urogenital system. After examining the patient and evaluating his complaints, the doctor may prescribe a consultation with other highly qualified specialists:
- venereologist (if you suspect a sexual infection);
- oncologist (if there are characteristic signs of the tumor process).

A complete laboratory and instrumental examination is required to establish a final diagnosis.
Diagnostics
The initial stage of the comprehensive examination is a thorough examination by a urologist:
- Visual assessment of the state of the genitals - the penis, head and foreskin, perineum. The aim of the examination is to detect injuries, deformities, seals, inflammations and skin rashes.
- Palpation in the groin area. They assess the condition of the lymph nodes, their size, density, and skin color.
- Prostate examination. The procedure is performed by inserting a finger into the anus. The goal is to identify seals in the prostate gland and take biological material for analysis.
- Collection of secretions from the urinary tract for vegetation and planting under a microscope - allows you to identify the source of the disease and understand the extent of the inflammatory process.
Then the patient must pass a clinical blood test and, if necessary, detailed biochemistry. Hardware diagnostics are also mandatory:
- Ultrasound of the kidneys, prostate and bladder;
- CT scan;
- urography.
Important!
If malignant tumors are suspected in the urogenital system, a man is prescribed a biopsy and a complete histological examination of the biological material is performed.
Treatment of pathological discharge
Heterogeneous, unnaturally colored discharge from the urethra is only a symptom of the disease. You need to treat the pathology that caused a change in the secret of the penis. Based on the type of negative processes in the urogenital system, doctors use several groups of drugs:
- Antifungals. It is used for candidal lesions.
- Antibiotics from the group of cephalosporins - used to treat gonorrhea, bacterial urethritis.
- Long-acting drugs.
- Anti-inflammatory antibiotics.
In addition to the drugs, the patient also receives vitamin complexes and immunostimulating drugs.
Prevention
In order to avoid the negative consequences of urogenital pathologies, it is important to observe preventive measures.
- Pay attention to hygiene. In order to prevent the proliferation of bacteria, it is important to wash the head of the penis thoroughly and push the foreskin back.
- Watch your intimate life. Stop promiscuity, always protect yourself.
- Empty the bladder in time to avoid overstretching.
- Avoid stress and emotional overload.
- Optimize physical activity - do not strain the body with hard work or excessive training.

It is necessary to eat right, eliminate bad habits and avoid hypothermia.
Normal discharge in men is clear or white in moderate amounts. The appearance of an unpleasant smell, pus or blood stains, the consistency of the vitreous becoming curd, sticky or watery are symptoms of pathological disorders of the organs of the urogenital system. To identify the causes of this condition, you should contact a urologist. After a thorough examination, the doctors prescribe the appropriate treatment.